I blogged before about the study by David Spence and colleagues, published online in July 2012 in the journal Atherosclerosis (). This study attracted a lot of media attention (e.g., ). The article is titled: “Egg yolk consumption and carotid plaque”. The study argues that “regular consumption of egg yolk should be avoided by persons at risk of cardiovascular disease”. It hints at egg yolks being unhealthy in general, possibly even more so than cigarettes.
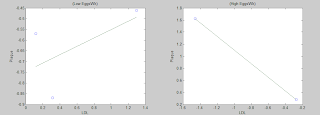
I used the numbers in Table 2 of the article (only 5 rows of data, one per quintile; i.e., N=5) to conduct a type of analysis that is rarely if ever conducted in health studies – a moderating effects analysis. A previous blog post summarizes the results of one such analysis using WarpPLS (). It looked into the effect of the number of eggs consumed per week on the association between blood LDL cholesterol and plaque (carotid plaque). The conclusion, which is admittedly tentative due to the small sample (N=5), was that plaque decreased as LDL cholesterol increased with consumption of 2.3 eggs per week or more ().
Recently I ran an analysis on the moderating effect of number of eggs consumed per week on the association between cumulative smoking (measured in “pack years”) and plaque. As it turns out, if you fit a 3D surface to the five data points that you get for these three variables from Table 2 of the article, you end up with a relatively smooth surface. Below is a 3D plot of the 5 data points, followed by a best-fitting 3D surface (developed using an experimental algorithm).
Based on this best-fitting surface you could then generate a contour graph, shown below. The “lines” are called “isolines”. Each isoline refers to plaque values that are constant for a set of eggs per week and cumulative smoking combinations. Next to the isolines are the corresponding plaque values. The first impression is indeed that both egg consumption and smoking are causing plaque buildup, as plaque clearly increases as one moves toward the top-right corner of the graph.
But focus your attention on each individual isoline, one at a time. It is clear that plaque remains constant for increases in cumulative smoking, as long as egg consumption increases. Take for example the isoline that refers to 120 mm2 of plaque area. An increase in cumulative smoking from about 14.5 to 16 pack years leads to no increase in plaque if egg consumption goes up from about 2 to 2.3 eggs per week.
These within-isoline trends, which are fairly stable across isolines (they are all slanted to the right), clearly contradict the idea that eggs cause plaque buildup. So, why does plaque buildup seem to clearly increase with egg consumption? Here is a good reason: egg consumption is very strongly correlated with age, and plaque increases with age. The correlation is a whopping 0.916. And I am not talking about cumulative egg consumption, which the authors also measure, through a variable called “egg-yolk years”. No, I am talking about eggs per week. In this dataset, older folks were eating more eggs, period.
The correlation between plaque and age is even higher: 0.977. Given this, it makes sense to look at individual isolines. This would be analogous to what biostatisticians often call “adjusting for age”, or analyzing the effect of egg consumption on plaque buildup “keeping age constant”. A different technique is to “control for age”; this technique would be preferable had the correlations been lower (say, lower than 0.7), as collinearity levels might have been below acceptable thresholds.
The underlying logic of the “keeping age constant” technique is fairly sound in the face of such a high correlation, which would make “controlling for age” very difficult due to collinearity. When we “keep age constant”, the results point at egg consumption being protective among smokers.
But diehard fans of the idea that eggs are unhealthy could explain the results differently. Maybe egg consumption causes plaque to go up, but smoking has a protective effect. Again taking the isoline that refers to 120 mm2 of plaque area, these diehard fans could say that an increase in egg consumption from 2 to 2.3 eggs per week leads to no increase in plaque if cumulative smoking goes up from about 14.5 to 16 pack years.
Not too long ago I also blogged about a medical case study of a man who ate approximately 25 eggs (20 to 30) per day for over 15 years (probably well over), was almost 90 years old (88) when the case was published in the prestigious The New England Journal of Medicine, and was in surprisingly good health (). This man was not a smoker.
Perhaps if this man smoked 25 cigarettes per day, and ate no eggs, he would be in even better health eh!?
Monday, December 24, 2012
Monday, December 10, 2012
Does tallness cause heart disease? No, but sex does
Popular beliefs about medical issues are sometimes motivated by a statistical phenomenon known as “spurious relationship”, among other names. Two variables X and Y are influenced by a third variable C, which leads to X and Y being correlated and thus the impression that X and Y are causally associated.
Take a look at the table below, which I blogged about in a previous post (). This table shows that there is a strong unadjusted correlation between height and arterial stiffness, a marker of heart disease. The likelihood that the correlation is due to chance is lower than one tenth of a percentage point (P<.001).
Interestingly, the authors of the study even use height as a control variable to narrow down the “true” causes of arterial stiffness (column with adjusted results), assuming that height did indeed influence arterial stiffness and what they found to be a key predictor of arterial stiffness, 2-hour postprandial glucose.
But there is no convincing evidence that height causes heart disease, with exception of pathological extremes – e.g., acromegaly. Extremes tend to influence statistical results somewhat, leading to conflicting conclusions that end up being disseminated by the popular media (). This is one of the sources of popular beliefs about medical issues.
Another, more important, source are real confounders. And this takes us back to the issue of height being associated with heart disease. In fact, height will typically be significantly associated with heart disease in almost any study that includes men and women and does not control for biological sex.
One of the reasons is that women overall tend to have a significantly lower incident of heart disease than men. The other is that height is significantly lower among women than men, on average, even though there are several women who are taller than the average man.
The table above was from a study including both sexes. Therefore, the strong association between height and arterial stiffness is a “reflection” of the strong association between being male and increased arterial stiffness. If one were to add a variable coded as 0 for male and 1 for female, and use it in a multivariate analysis of predictor of arterial stiffness, together with height, the effect of height would probably “disappear”.
Biological sex is the control variable, the “confounder”, that the authors should have used to narrow down the “true” causes of arterial stiffness (second column in the table). In the absence of biological sex, controlling for height accomplished something similar, but in a “wobbly” way, leaving many readers scratching their heads in confusion.
Take a look at the table below, which I blogged about in a previous post (). This table shows that there is a strong unadjusted correlation between height and arterial stiffness, a marker of heart disease. The likelihood that the correlation is due to chance is lower than one tenth of a percentage point (P<.001).
Interestingly, the authors of the study even use height as a control variable to narrow down the “true” causes of arterial stiffness (column with adjusted results), assuming that height did indeed influence arterial stiffness and what they found to be a key predictor of arterial stiffness, 2-hour postprandial glucose.
But there is no convincing evidence that height causes heart disease, with exception of pathological extremes – e.g., acromegaly. Extremes tend to influence statistical results somewhat, leading to conflicting conclusions that end up being disseminated by the popular media (). This is one of the sources of popular beliefs about medical issues.
Another, more important, source are real confounders. And this takes us back to the issue of height being associated with heart disease. In fact, height will typically be significantly associated with heart disease in almost any study that includes men and women and does not control for biological sex.
One of the reasons is that women overall tend to have a significantly lower incident of heart disease than men. The other is that height is significantly lower among women than men, on average, even though there are several women who are taller than the average man.
The table above was from a study including both sexes. Therefore, the strong association between height and arterial stiffness is a “reflection” of the strong association between being male and increased arterial stiffness. If one were to add a variable coded as 0 for male and 1 for female, and use it in a multivariate analysis of predictor of arterial stiffness, together with height, the effect of height would probably “disappear”.
Biological sex is the control variable, the “confounder”, that the authors should have used to narrow down the “true” causes of arterial stiffness (second column in the table). In the absence of biological sex, controlling for height accomplished something similar, but in a “wobbly” way, leaving many readers scratching their heads in confusion.
Labels:
arterial stiffness,
diabetes,
gender,
glucose,
heart disease
Tuesday, November 27, 2012
Facebook Revisited: Does the Platform Help or Hurt Users (or Both)?
The benefits and challenges of social media for public health are a frequent topic on Pop Health. For example, I've explored the influence of these platforms on emergency response, increasing the number of organ donors, and health activism. However, one of the debates that I hear the most among public health colleagues relates to Facebook.
Does it isolate users? Does it connect users? Does it do both?
Earlier this year, my colleague Elana Premack Sandler explored this debate as it relates to loneliness. Inspired by a feature in the Atlantic Magazine, Elana asks key questions like, "Is Facebook part of the separating or part of the congregating?" She also mentions concerns about how Facebook (and other social media platforms) affect our social skills and therefore our friendships.
I thought of Elana's writing as I read a new post on the Atlantic website today, "Are Your Facebook Friends Stressing You Out? (Yes.)". This post highlights a new report out from the University of Edinburgh Business School. The report caught my eye because it identified a very specific cause of stress for Facebook users. The more groups of "friends" a user had (e.g., family, real life friends, co-workers, etc), the more anxiety they had because there was a greater chance of offending someone with their posts. The report stated that the greatest anxiety came from adding parents or employers as Facebook "friends". As Megan Garber writes so eloquently in her Atlantic post, the stress comes from Facebook forcing users to "conduct our digital lives with singular identities". The way we speak or act around family or friends or co-workers must jive on Facebook, or we run the risk of offending someone. I'm sure many of us saw this conflict a few weeks ago when political and election posts ran rampant on Facebook!
The anxiety described above is interesting, because ideally what we would hope is that Facebook provides a source of social support to users. Social support occurs when one is cared for by others (via emotional, tangible, or informational support). The presence or absence of social support is a factor related to public health issues, such as suicide.
So after reading through the various posts/articles, what do I think about my opening questions about Facebook?
Does it isolate users? Does it connect users? Does it do both?
I think it does both. I have seen it do both. For example:
Isolation: I have spoken to friends and colleagues who feel terrible about themselves or their lives after scrolling through their Facebook news feed. A friend with chronic illness feels isolated hearing about the latest vacation or new job taken by her "friends". A friend suffering from infertility can't bear one more picture of a "friend" and their newborn. I think much of this results from the "whitewash" that many of us put on Facebook. We often paint a picture for our Facebook friends, full of engagements and babies and fun events.
Connection: Earlier this year I watched a suicide intervention unfold on Facebook via the comment section under a post. A friend of a friend posted a suicidal message on their Facebook wall. Within minutes, "friends" reached out in the comments. However, not only did they "speak" to the person, but they interacted with each other and followed up in real life. One comment read, "Did someone go to his house?" The next comment read, "I went to his house and I called his parents". After he was taken to the hospital, a comment was posted to inform all the friends that he was safe. As a public health practitioner that worked in suicide prevention for years, I was amazed with what I saw.
So what can we do to reduce the isolation/anxiety and increase the connection? You can certainly start by exerting your control over your Facebook account. For example:
Does it isolate users? Does it connect users? Does it do both?
Earlier this year, my colleague Elana Premack Sandler explored this debate as it relates to loneliness. Inspired by a feature in the Atlantic Magazine, Elana asks key questions like, "Is Facebook part of the separating or part of the congregating?" She also mentions concerns about how Facebook (and other social media platforms) affect our social skills and therefore our friendships.
I thought of Elana's writing as I read a new post on the Atlantic website today, "Are Your Facebook Friends Stressing You Out? (Yes.)". This post highlights a new report out from the University of Edinburgh Business School. The report caught my eye because it identified a very specific cause of stress for Facebook users. The more groups of "friends" a user had (e.g., family, real life friends, co-workers, etc), the more anxiety they had because there was a greater chance of offending someone with their posts. The report stated that the greatest anxiety came from adding parents or employers as Facebook "friends". As Megan Garber writes so eloquently in her Atlantic post, the stress comes from Facebook forcing users to "conduct our digital lives with singular identities". The way we speak or act around family or friends or co-workers must jive on Facebook, or we run the risk of offending someone. I'm sure many of us saw this conflict a few weeks ago when political and election posts ran rampant on Facebook!
The anxiety described above is interesting, because ideally what we would hope is that Facebook provides a source of social support to users. Social support occurs when one is cared for by others (via emotional, tangible, or informational support). The presence or absence of social support is a factor related to public health issues, such as suicide.
So after reading through the various posts/articles, what do I think about my opening questions about Facebook?
Does it isolate users? Does it connect users? Does it do both?
I think it does both. I have seen it do both. For example:
Isolation: I have spoken to friends and colleagues who feel terrible about themselves or their lives after scrolling through their Facebook news feed. A friend with chronic illness feels isolated hearing about the latest vacation or new job taken by her "friends". A friend suffering from infertility can't bear one more picture of a "friend" and their newborn. I think much of this results from the "whitewash" that many of us put on Facebook. We often paint a picture for our Facebook friends, full of engagements and babies and fun events.
Connection: Earlier this year I watched a suicide intervention unfold on Facebook via the comment section under a post. A friend of a friend posted a suicidal message on their Facebook wall. Within minutes, "friends" reached out in the comments. However, not only did they "speak" to the person, but they interacted with each other and followed up in real life. One comment read, "Did someone go to his house?" The next comment read, "I went to his house and I called his parents". After he was taken to the hospital, a comment was posted to inform all the friends that he was safe. As a public health practitioner that worked in suicide prevention for years, I was amazed with what I saw.
So what can we do to reduce the isolation/anxiety and increase the connection? You can certainly start by exerting your control over your Facebook account. For example:
- Create a policy about "groups of friends" that you accept into your circle. I know lots of people that do not accept requests from co-workers or parents. They make it clear to the individual that it is nothing personal, they just have minimal friends with which they share intimate information.
- Use the privacy settings! You can control who can see your posts.
- Find and use the unfriend button! I have done this frequently. If someone posts messages that are offensive or disrespectful regarding something that I've posted- I get rid of them quickly.
- Take a break from Facebook. If you realize that Facebook is making you feel bad about yourself, take a break or disable your account. Use that time to connect with your in real life (IRL) friends or family.
Tell me what you think!
- Does Facebook isolate and stress us?
- Does Facebook connect us?
- What other strategies can help to reduce the isolation and increase the connection on Facebook or other social media platforms?
Labels:
Facebook,
mental health,
public health,
social media,
social networks
Monday, November 26, 2012
No fat gain while eating well during the Holiday Season: Palatability isolines, the 14-percent advantage, and nature’s special spice
Like most animals, our Paleolithic ancestors had to regularly undergo short periods of low calorie intake. If they were successful at procuring food, those ancestors alternated between periods of mild famine and feast. As a result, nature allowed them to survive and leave offspring. The periods of feast likely involved higher-than-average consumption of animal foods, with the opposite probably being true in periods of mild famine.
Almost anyone who adopted a low carbohydrate diet for a while will tell you that they find foods previously perceived as bland, such as carrots or walnuts, to taste very sweet – meaning, to taste very good. This is a special case of a more general phenomenon. If a nutrient is important for your body, and your body is deficient in it, those foods that contain the nutrient will taste very good.
This rule of thumb applies primarily to foods that contributed to selection pressures in our evolutionary past. Mostly these were foods available in our Paleolithic evolutionary past, although some populations may have developed divergent partial adaptations to more modern foods due to recent yet acute selection pressure. Because of the complexity of the dietary nutrient absorption process, involving many genes, I suspect that the vast majority of adaptations to modern foods are partial adaptations.
Modern engineered foods are designed to bypass reward mechanisms that match nutrient content with deficiency levels. That is not the case with more natural foods, which tend to taste good only to the extent that the nutrients that they carry are needed by our bodies.
Consequently palatability is not fixed for a particular natural food; it does not depend only on the nutrient content of the food. It also depends on the body’s deficiency with respect to the nutrient that the food contains. Below is what you would get if you were to plot a surface that best fit a set of data points relating palatability of a specific food item, nutrient content of that food, and the level of nutrient deficiency, for a group of people. I generated the data through a simple simulation, with added error to make the simulation more realistic.
Based on this best-fitting surface you could then generate a contour graph, shown below. The curves are “contour lines”, a.k.a. isolines. Each isoline refers to palatability values that are constant for a set of nutrient content and nutrient deficiency combinations. Next to the isolines are the corresponding palatability values, which vary from about 10 to 100. As you can see, palatability generally goes up as one moves toward to right-top corner of the graph, which is the area where nutrient content and nutrient deficiency are both high.
What happens when the body is in short-term nutrient deficiency with respect to a nutrient? One thing that happens is an increase in enzymatic activity, often referred to by the more technical term “phosphorylation”. Enzymes are typically proteins that cause an acute and targeted increase in specific metabolic processes. Many diseases are associated with dysfunctional enzyme activity. Short-term nutrient deficiency causes enzymatic activity associated with absorption and retention of the nutrient to go up significantly. In other words, your body holds on to its reserves of the nutrient, and becomes much more responsive to dietary intake of the nutrient.
The result is predictable, but many people seem to be unaware of it; most are actually surprised by it. If the nutrient in question is a macro-nutrient, it will be allocated in such a way that less of it will go into our calorie stores – namely adipocytes (body fat). This applies even to dietary fat itself, as fat is needed throughout the body for functions other than energy storage. I have heard from many people who, by alternating between short-term fasting and feasting, lost body fat while maintaining the same calorie intake as in a previous period when they were steadily gaining body fat without any fasting. Invariably they were very surprised by what happened.
In a diet of mostly natural foods, with minimal intake of industrialized foods, short-term calorie deficiency is usually associated with short-term deficiency of various nutrients. Short-term calorie deficiency, when followed by significant calorie surplus (i.e., eating little and then a lot), is associated with a phenomenon I blogged about before here – the “14-percent advantage” of eating little and then a lot (, ). Underfeeding and then overfeeding leads to a reduction in the caloric value of the meals during overfeeding; a reduction of about 14 percent of the overfed amount.
So, how can you go through the Holiday Season giving others the impression that you eat as much as you want, and do not gain any body fat (maybe even lose some)? Eat very little, or fast, in those days where there will be a feast (Thanksgiving dinner); and then eat to satisfaction during the feast, staying away from industrialized foods as much as possible. Everything will taste extremely delicious, as nature’s “special spice” is hunger. And you may even lose body fat in the process!
But there is a problem. Our bodies are not designed to associate eating very little, or not at all, with pleasure. Yet another thing that we can blame squarely on evolution! Success takes practice and determination, aided by the expectation of delayed gratification.
Almost anyone who adopted a low carbohydrate diet for a while will tell you that they find foods previously perceived as bland, such as carrots or walnuts, to taste very sweet – meaning, to taste very good. This is a special case of a more general phenomenon. If a nutrient is important for your body, and your body is deficient in it, those foods that contain the nutrient will taste very good.
This rule of thumb applies primarily to foods that contributed to selection pressures in our evolutionary past. Mostly these were foods available in our Paleolithic evolutionary past, although some populations may have developed divergent partial adaptations to more modern foods due to recent yet acute selection pressure. Because of the complexity of the dietary nutrient absorption process, involving many genes, I suspect that the vast majority of adaptations to modern foods are partial adaptations.
Modern engineered foods are designed to bypass reward mechanisms that match nutrient content with deficiency levels. That is not the case with more natural foods, which tend to taste good only to the extent that the nutrients that they carry are needed by our bodies.
Consequently palatability is not fixed for a particular natural food; it does not depend only on the nutrient content of the food. It also depends on the body’s deficiency with respect to the nutrient that the food contains. Below is what you would get if you were to plot a surface that best fit a set of data points relating palatability of a specific food item, nutrient content of that food, and the level of nutrient deficiency, for a group of people. I generated the data through a simple simulation, with added error to make the simulation more realistic.
Based on this best-fitting surface you could then generate a contour graph, shown below. The curves are “contour lines”, a.k.a. isolines. Each isoline refers to palatability values that are constant for a set of nutrient content and nutrient deficiency combinations. Next to the isolines are the corresponding palatability values, which vary from about 10 to 100. As you can see, palatability generally goes up as one moves toward to right-top corner of the graph, which is the area where nutrient content and nutrient deficiency are both high.
What happens when the body is in short-term nutrient deficiency with respect to a nutrient? One thing that happens is an increase in enzymatic activity, often referred to by the more technical term “phosphorylation”. Enzymes are typically proteins that cause an acute and targeted increase in specific metabolic processes. Many diseases are associated with dysfunctional enzyme activity. Short-term nutrient deficiency causes enzymatic activity associated with absorption and retention of the nutrient to go up significantly. In other words, your body holds on to its reserves of the nutrient, and becomes much more responsive to dietary intake of the nutrient.
The result is predictable, but many people seem to be unaware of it; most are actually surprised by it. If the nutrient in question is a macro-nutrient, it will be allocated in such a way that less of it will go into our calorie stores – namely adipocytes (body fat). This applies even to dietary fat itself, as fat is needed throughout the body for functions other than energy storage. I have heard from many people who, by alternating between short-term fasting and feasting, lost body fat while maintaining the same calorie intake as in a previous period when they were steadily gaining body fat without any fasting. Invariably they were very surprised by what happened.
In a diet of mostly natural foods, with minimal intake of industrialized foods, short-term calorie deficiency is usually associated with short-term deficiency of various nutrients. Short-term calorie deficiency, when followed by significant calorie surplus (i.e., eating little and then a lot), is associated with a phenomenon I blogged about before here – the “14-percent advantage” of eating little and then a lot (, ). Underfeeding and then overfeeding leads to a reduction in the caloric value of the meals during overfeeding; a reduction of about 14 percent of the overfed amount.
So, how can you go through the Holiday Season giving others the impression that you eat as much as you want, and do not gain any body fat (maybe even lose some)? Eat very little, or fast, in those days where there will be a feast (Thanksgiving dinner); and then eat to satisfaction during the feast, staying away from industrialized foods as much as possible. Everything will taste extremely delicious, as nature’s “special spice” is hunger. And you may even lose body fat in the process!
But there is a problem. Our bodies are not designed to associate eating very little, or not at all, with pleasure. Yet another thing that we can blame squarely on evolution! Success takes practice and determination, aided by the expectation of delayed gratification.
Labels:
body fat,
calorie restriction,
dietary fat,
fasting,
fat loss,
Holiday Season,
intermittent fasting,
paleo diet
Monday, November 12, 2012
The bipolar disorder pendulum: Depression as a compensatory adaptation
As far as explaining natural phenomena, Darwin was one of the best theoretical researchers of all time. Yet, there were a few phenomena that puzzled him for many years. One was the evolution of survival-impairing traits such as the peacock’s train, the large and brightly colored tail appendage observed in males.
Tha male peacock’s train is detrimental to the animal’s survival, and yet it is clearly an evolved trait ().
This type of trait is known as a “costly” trait – a trait that enhances biological fitness (or reproductive success, not to be confused with “gym fitness”), and yet is detrimental to the survival of the individuals who possess it (). Many costly traits have evolved in animals because of sexual selection. That is, they have evolved because they are sexy.
Costly traits seem like a contradiction in terms, but the mechanisms by which they can evolve become clear when evolution is modeled mathematically (, ). There is evidence that mental disorders may have evolved as costs of attractive mental traits (); one in particular, bipolar disorder (a.k.a. manic-depression), fits this hypothesis quite well.
Ironically, a key contributor to the mathematics used to understand costly traits, George R. Price (), might have suffered from severe bipolar disorder. Most of Price’s work in evolutionary biology was done in the 1970s; toward the end of his life, which was untimely ended by Price himself. For many years he was known mostly by evolutionary biologists, but this has changed recently with the publication of Oren Harman’s superb biographical book titled “The Price of Altruism: George Price and the Search for the Origins of Kindness” ().
Bipolar disorder is a condition characterized by disruptive mood swings. These swings are between manic and depressed states, and are analogous to the movement of a pendulum in that they alternate, seemingly gravitating around the "normal" state. See the figurative pendulum representation below, adapted from a drawing on Thinkquest.org.
Bipolar disorder is generally associated with creative intelligence, which is a very attractive trait (). Moreover, the manic state of the disorder is associated with hypersexuality and exaggerated generosity (). So one can clearly see how having bipolar disorder may lead to greater reproductive success, even as it creates long-term survival problems.
On one hand, a person may become very energetic and creative while in the manic state. This could be one of the reasons why many who suffer from bipolar disorder have fairly successful careers in fields that require creative intelligence (), which are many and not restricted to fields related to the fine and performing arts. Creative intelligence is highly valued in most knowledge-intensive professions ().
On the other hand, sustained acute mania or depression are frequently associated with serious health problems (). This is why the clinical treatment of bipolar disorder often starts with an attempt to keep the pendulum from moving too far in one direction or another. This may require medication, such as clinical doses of the elemental salt lithium, prior to cognitive behavioral therapy. The focus of cognitive behavioral therapy is on changing the way one sees and thinks about the world, particularly one’s “social world”.
Prolonged acute mania, usually accompanied by severely impaired sleep, may lead to psychosis. This, psychosis, is an extreme state characterized by hallucinations and/or delusions, leading to hospitalization in most cases. It has been theorized that depression is an involuntary compensatory adaptation () aimed at moving the pendulum in the other direction, out of the manic state, before more damage ensues ().
Elaborate approaches have been devised to treat and manage bipolar disorder treatment that involve the identification of mania and depression “prodromes” (), which are signs that a full-blown manic or depressive episode is about to start. Once prodromes are identified, cognitive behavioral therapy techniques are employed to prevent the pendulum from moving further in one direction or the other. The main goal of these techniques is to change one’s way of thinking about various issues (e.g., fears, pessimism). These techniques take years of practice to be used effectively.
Identification of prodromes and subsequent use of cognitive behavioral therapy seems to be particularly effective when dutifully applied with respect to manic episodes (). The reason for this may be related to one interesting fact related to bipolar disorder: manic episodes are not normally dreaded as much as depression episodes.
In fact, many sufferers avoid taking medication because they do not want to give up the creative and energetic bursts that come with manic episodes, even though they absolutely do not want the pendulum to go in the other direction. The problem is that, if depression is indeed a compensatory adaptation to mania, it seems reasonable to assume that extreme manic episodes are likely to be followed by extreme episodes of depression. Perhaps the key to avoid prolonged acute depression is to avoid prolonged acute mania.
As someone with bipolar disorder becomes more and more excited with novel and racing thoughts (a prodrome of mania), it would probably make sense to identify and carry out calming activities – to avoid a fall into despairing depression afterwards.
Tha male peacock’s train is detrimental to the animal’s survival, and yet it is clearly an evolved trait ().
This type of trait is known as a “costly” trait – a trait that enhances biological fitness (or reproductive success, not to be confused with “gym fitness”), and yet is detrimental to the survival of the individuals who possess it (). Many costly traits have evolved in animals because of sexual selection. That is, they have evolved because they are sexy.
Costly traits seem like a contradiction in terms, but the mechanisms by which they can evolve become clear when evolution is modeled mathematically (, ). There is evidence that mental disorders may have evolved as costs of attractive mental traits (); one in particular, bipolar disorder (a.k.a. manic-depression), fits this hypothesis quite well.
Ironically, a key contributor to the mathematics used to understand costly traits, George R. Price (), might have suffered from severe bipolar disorder. Most of Price’s work in evolutionary biology was done in the 1970s; toward the end of his life, which was untimely ended by Price himself. For many years he was known mostly by evolutionary biologists, but this has changed recently with the publication of Oren Harman’s superb biographical book titled “The Price of Altruism: George Price and the Search for the Origins of Kindness” ().
Bipolar disorder is a condition characterized by disruptive mood swings. These swings are between manic and depressed states, and are analogous to the movement of a pendulum in that they alternate, seemingly gravitating around the "normal" state. See the figurative pendulum representation below, adapted from a drawing on Thinkquest.org.
Bipolar disorder is generally associated with creative intelligence, which is a very attractive trait (). Moreover, the manic state of the disorder is associated with hypersexuality and exaggerated generosity (). So one can clearly see how having bipolar disorder may lead to greater reproductive success, even as it creates long-term survival problems.
On one hand, a person may become very energetic and creative while in the manic state. This could be one of the reasons why many who suffer from bipolar disorder have fairly successful careers in fields that require creative intelligence (), which are many and not restricted to fields related to the fine and performing arts. Creative intelligence is highly valued in most knowledge-intensive professions ().
On the other hand, sustained acute mania or depression are frequently associated with serious health problems (). This is why the clinical treatment of bipolar disorder often starts with an attempt to keep the pendulum from moving too far in one direction or another. This may require medication, such as clinical doses of the elemental salt lithium, prior to cognitive behavioral therapy. The focus of cognitive behavioral therapy is on changing the way one sees and thinks about the world, particularly one’s “social world”.
Prolonged acute mania, usually accompanied by severely impaired sleep, may lead to psychosis. This, psychosis, is an extreme state characterized by hallucinations and/or delusions, leading to hospitalization in most cases. It has been theorized that depression is an involuntary compensatory adaptation () aimed at moving the pendulum in the other direction, out of the manic state, before more damage ensues ().
Elaborate approaches have been devised to treat and manage bipolar disorder treatment that involve the identification of mania and depression “prodromes” (), which are signs that a full-blown manic or depressive episode is about to start. Once prodromes are identified, cognitive behavioral therapy techniques are employed to prevent the pendulum from moving further in one direction or the other. The main goal of these techniques is to change one’s way of thinking about various issues (e.g., fears, pessimism). These techniques take years of practice to be used effectively.
Identification of prodromes and subsequent use of cognitive behavioral therapy seems to be particularly effective when dutifully applied with respect to manic episodes (). The reason for this may be related to one interesting fact related to bipolar disorder: manic episodes are not normally dreaded as much as depression episodes.
In fact, many sufferers avoid taking medication because they do not want to give up the creative and energetic bursts that come with manic episodes, even though they absolutely do not want the pendulum to go in the other direction. The problem is that, if depression is indeed a compensatory adaptation to mania, it seems reasonable to assume that extreme manic episodes are likely to be followed by extreme episodes of depression. Perhaps the key to avoid prolonged acute depression is to avoid prolonged acute mania.
As someone with bipolar disorder becomes more and more excited with novel and racing thoughts (a prodrome of mania), it would probably make sense to identify and carry out calming activities – to avoid a fall into despairing depression afterwards.
Monday, October 29, 2012
The man who ate 25 eggs per day: What does this case really tell us?
Many readers of this blog have probably heard about the case of the man who ate approximately 25 eggs (20 to 30) per day for over 15 years (probably well over), was almost 90 years old (88) when the case was published in the prestigious The New England Journal of Medicine, and was in surprisingly good health ().
The case was authored by the late Dr. Fred Kern, Jr., a widely published lipid researcher after whom the Kern Lipid Conference is named (). One of Kern’s research interests was bile, a bitter-tasting fluid produced by the liver (and stored in the gallbladder) that helps with the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. He frames the man’s case in terms of a compensatory adaptation tied to bile secretion, arguing that this man was rather unique in his ability to deal with a lethal daily dose of dietary cholesterol.
Kern seemed to believe that dietary cholesterol was harmful, but that this man was somehow “immune” to it. This is ironic, because often this case is presented as evidence against the hypothesis that dietary cholesterol can be harmful. The table below shows the general nutrient content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. The numbers in this and other tables are based on data from Nutritiondata.com (), in some cases triangulated with other data. The 5.3 g of cholesterol in the table (i.e., 5,300 mg) is 1,775 percent the daily value recommended by the Institute of Medicine of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences ().
As you can see, the man was on a very low carbohydrate diet with a high daily intake of fat and protein. The man is described as an: “… 88-year-old man who lived in a retirement community [and] complained only of loneliness since his wife's death. He was an articulate, well-educated elderly man, healthy except for an extremely poor memory without other specific neurologic deficits … His general health had been excellent, without notable symptoms. He had mild constipation.”
The description does not suggest inherited high longevity: “His weight had been constant at 82 to 86 kg (height, 1.87 m). He had no history (according to the patient and his personal physician of 15 years) of heart disease, stroke, or kidney disease … The patient had never smoked and never drank excessively. His father died of unknown causes at the age of 40, and his mother died at 76 … He kept a careful record, egg by egg, of the number ingested each day …”
The table below shows the fat content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. With over 14 g of omega-6 fat intake every day, this man was probably close to or in “industrial seed oils territory” (), as far as daily omega-6 fat intake is concerned. And the intake of omega-3 fats, at less than 1 g, was not nearly enough to balance it. However, here is a relevant fact – this man was not consuming any industrial seed oils. He liked his eggs soft-boiled, which is why the numbers in this post refer to boiled eggs.
This man weighed between 82 to 86 kg, which is about 180 to 190 lbs. His height was 1.87 m, or about 6 ft 1 in. Therefore his body mass index varied between approximately 23 and 25, which is in the normal range. In other words, this person was not even close to obese during the many years he consumed 25 eggs or so per day. In the comments section of a previous post, on the sharp increase in obesity since the 1980s (), several readers argued that the sharp increase in obesity was very likely caused by an increase in omega-6 fat consumption.
I am open to the idea that industrialized omega-6 fats played a role in the sharp increase in obesity observed since the 1980s. When it comes to omega-6 fat consumption in general, including that in “more natural” foods (e.g., poultry and eggs), I am more skeptical. Still, it is quite possible that a diet high in omega-6 fats in general is unhealthy primarily if it is devoid of other nutrients. This man’s overall diet might have been protective not because of what he was not eating, but because of what he was eating.
The current debates pitting one diet against another often revolve around the ability of one diet or another to eliminate or reduce the intake of a “bad thing” (e.g., cholesterol, saturated fat, carbohydrates). Perhaps the discussion should be more focused on, or at least not completely ignore, what one diet or another include as protective factors. This would help better explain “odd findings”, such as the lowest-mortality body mass index of 26 in urban populations (). It would also help better explain “surprising cases”; such as this 25-eggs-a-day man’s, vegetarian-vegan “ageless woman” Annette Larkins’s (), and the decidedly carnivore De Vany couple’s ().
The table below shows the vitamin content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. The vitamin K2 content provided by Nutritiondata.com was incorrect; I had to get what seems to be the right number by triangulating values taken from various publications. And here we see something interesting. This man was consuming approximately the equivalent in vitamin K2 that one would get by eating 4 ounces of foie gras () every day. Foie gras, the fatty liver of overfed geese, is the richest known animal source of vitamin K2. This man’s diet was also high in vitamin A, which is believed to act synergistically with vitamin K2 – see Chris Masterjohn’s article on Weston Price’s “activator X” ().
Kern argued that the very high intake of dietary cholesterol led to a sharp increase in bile secretion, as the body tried to “get rid” of cholesterol (which is used in the synthesis of bile). However, the increased bile secretion might have been also been due to the high fat content of this man’s diet, since one of the main functions of bile is digestion of fats. Whatever the case may be, increased bile secretion leads to increased absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and vitamins K2 and A are fat-soluble vitamins that seem to be protective against cardiovascular disease, cancer and other degenerative diseases.
Finally, the table below shows the mineral content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. As you can see, this man consumed 550 percent the officially recommended daily intake of selenium. This intake was slightly lower than the 400 micrograms per day purported to cause selenosis in adults (). Similarly to vitamins K2 and A, selenium seems to be protective against cardiovascular disease, cancer and other degenerative diseases. This man’s diet was also rich in phosphorus, needed for healthy teeth and bones.
Not too many people live to be 88 years of age; many fewer reach that age in fairly good health. The country with the highest average life expectancy in the world at the time of this writing is Japan, with a life expectancy of about 82 years (79 for men, and 86 for women). Those who think that they need a high HDL cholesterol and a low LDL cholesterol to be in good health, and thus live long lives, may be surprised at this man’s lipid profile: “The patient's plasma lipid levels were normal: total cholesterol, 5.18 mmol per liter (200 mg per deciliter); LDL, 3.68 mmol per liter (142 mg per deciliter); and HDL, 1.17 mmol per liter (45 mg per deciliter). The ratio of LDL to HDL cholesterol was 3.15.”
If we assume that this man is at least somewhat representative of the human species, and not a major exception as Kern argued, this case tells us that a diet of 25 eggs per day followed by over 15 years may actually be healthy for humans. Such diet has the following features:
- It is very high in dietary cholesterol.
- It involves a high intake of omega-6 fats from animal sources, with none coming from industrial seed oils.
- It involves a high overall intake of fats, including saturated fats.
- It is fairly high in protein, all of which from animal sources.
- It is a very low carbohydrate diet, with no sugar in it.
- It is a nutritious diet, rich in vitamins K2 and A, as well as in selenium and phosphorus.
This man ate 25 eggs per day apparently due to an obsession tied to mental problems. Repeated attempts at changing his behavior were unsuccessful. He said: “Eating these eggs ruins my life, but I can't help it.”
The case was authored by the late Dr. Fred Kern, Jr., a widely published lipid researcher after whom the Kern Lipid Conference is named (). One of Kern’s research interests was bile, a bitter-tasting fluid produced by the liver (and stored in the gallbladder) that helps with the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. He frames the man’s case in terms of a compensatory adaptation tied to bile secretion, arguing that this man was rather unique in his ability to deal with a lethal daily dose of dietary cholesterol.
Kern seemed to believe that dietary cholesterol was harmful, but that this man was somehow “immune” to it. This is ironic, because often this case is presented as evidence against the hypothesis that dietary cholesterol can be harmful. The table below shows the general nutrient content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. The numbers in this and other tables are based on data from Nutritiondata.com (), in some cases triangulated with other data. The 5.3 g of cholesterol in the table (i.e., 5,300 mg) is 1,775 percent the daily value recommended by the Institute of Medicine of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences ().
As you can see, the man was on a very low carbohydrate diet with a high daily intake of fat and protein. The man is described as an: “… 88-year-old man who lived in a retirement community [and] complained only of loneliness since his wife's death. He was an articulate, well-educated elderly man, healthy except for an extremely poor memory without other specific neurologic deficits … His general health had been excellent, without notable symptoms. He had mild constipation.”
The description does not suggest inherited high longevity: “His weight had been constant at 82 to 86 kg (height, 1.87 m). He had no history (according to the patient and his personal physician of 15 years) of heart disease, stroke, or kidney disease … The patient had never smoked and never drank excessively. His father died of unknown causes at the age of 40, and his mother died at 76 … He kept a careful record, egg by egg, of the number ingested each day …”
The table below shows the fat content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. With over 14 g of omega-6 fat intake every day, this man was probably close to or in “industrial seed oils territory” (), as far as daily omega-6 fat intake is concerned. And the intake of omega-3 fats, at less than 1 g, was not nearly enough to balance it. However, here is a relevant fact – this man was not consuming any industrial seed oils. He liked his eggs soft-boiled, which is why the numbers in this post refer to boiled eggs.
This man weighed between 82 to 86 kg, which is about 180 to 190 lbs. His height was 1.87 m, or about 6 ft 1 in. Therefore his body mass index varied between approximately 23 and 25, which is in the normal range. In other words, this person was not even close to obese during the many years he consumed 25 eggs or so per day. In the comments section of a previous post, on the sharp increase in obesity since the 1980s (), several readers argued that the sharp increase in obesity was very likely caused by an increase in omega-6 fat consumption.
I am open to the idea that industrialized omega-6 fats played a role in the sharp increase in obesity observed since the 1980s. When it comes to omega-6 fat consumption in general, including that in “more natural” foods (e.g., poultry and eggs), I am more skeptical. Still, it is quite possible that a diet high in omega-6 fats in general is unhealthy primarily if it is devoid of other nutrients. This man’s overall diet might have been protective not because of what he was not eating, but because of what he was eating.
The current debates pitting one diet against another often revolve around the ability of one diet or another to eliminate or reduce the intake of a “bad thing” (e.g., cholesterol, saturated fat, carbohydrates). Perhaps the discussion should be more focused on, or at least not completely ignore, what one diet or another include as protective factors. This would help better explain “odd findings”, such as the lowest-mortality body mass index of 26 in urban populations (). It would also help better explain “surprising cases”; such as this 25-eggs-a-day man’s, vegetarian-vegan “ageless woman” Annette Larkins’s (), and the decidedly carnivore De Vany couple’s ().
The table below shows the vitamin content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. The vitamin K2 content provided by Nutritiondata.com was incorrect; I had to get what seems to be the right number by triangulating values taken from various publications. And here we see something interesting. This man was consuming approximately the equivalent in vitamin K2 that one would get by eating 4 ounces of foie gras () every day. Foie gras, the fatty liver of overfed geese, is the richest known animal source of vitamin K2. This man’s diet was also high in vitamin A, which is believed to act synergistically with vitamin K2 – see Chris Masterjohn’s article on Weston Price’s “activator X” ().
Kern argued that the very high intake of dietary cholesterol led to a sharp increase in bile secretion, as the body tried to “get rid” of cholesterol (which is used in the synthesis of bile). However, the increased bile secretion might have been also been due to the high fat content of this man’s diet, since one of the main functions of bile is digestion of fats. Whatever the case may be, increased bile secretion leads to increased absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and vitamins K2 and A are fat-soluble vitamins that seem to be protective against cardiovascular disease, cancer and other degenerative diseases.
Finally, the table below shows the mineral content of the man’s daily diet of eggs. As you can see, this man consumed 550 percent the officially recommended daily intake of selenium. This intake was slightly lower than the 400 micrograms per day purported to cause selenosis in adults (). Similarly to vitamins K2 and A, selenium seems to be protective against cardiovascular disease, cancer and other degenerative diseases. This man’s diet was also rich in phosphorus, needed for healthy teeth and bones.
Not too many people live to be 88 years of age; many fewer reach that age in fairly good health. The country with the highest average life expectancy in the world at the time of this writing is Japan, with a life expectancy of about 82 years (79 for men, and 86 for women). Those who think that they need a high HDL cholesterol and a low LDL cholesterol to be in good health, and thus live long lives, may be surprised at this man’s lipid profile: “The patient's plasma lipid levels were normal: total cholesterol, 5.18 mmol per liter (200 mg per deciliter); LDL, 3.68 mmol per liter (142 mg per deciliter); and HDL, 1.17 mmol per liter (45 mg per deciliter). The ratio of LDL to HDL cholesterol was 3.15.”
If we assume that this man is at least somewhat representative of the human species, and not a major exception as Kern argued, this case tells us that a diet of 25 eggs per day followed by over 15 years may actually be healthy for humans. Such diet has the following features:
- It is very high in dietary cholesterol.
- It involves a high intake of omega-6 fats from animal sources, with none coming from industrial seed oils.
- It involves a high overall intake of fats, including saturated fats.
- It is fairly high in protein, all of which from animal sources.
- It is a very low carbohydrate diet, with no sugar in it.
- It is a nutritious diet, rich in vitamins K2 and A, as well as in selenium and phosphorus.
This man ate 25 eggs per day apparently due to an obsession tied to mental problems. Repeated attempts at changing his behavior were unsuccessful. He said: “Eating these eggs ruins my life, but I can't help it.”
Labels:
BMI,
cholesterol,
egg,
longevity,
obesity,
omega-6,
omega-6 to omega-3 ratio
Thursday, October 25, 2012
October is [Fill in the Blank] Awareness Month- A Guest Post for "The Public's Health"
Today I had the pleasure contributing another guest post on "The Public's Health". The blog is a collaboration between the Drexel University School of Public Health and Philly.com. In multiple posts each week, the authors highlight contemporary, historical, and ethical matters that challenge public health professionals.
In today's post, I examine health "awareness campaigns" and discuss their effectiveness for improving public health.
What do you think: Is the public burned out on annual health observances? Or are they effective in helping to prevent illness/disease? In what other ways can organizations and individuals become more action-oriented to help improve the public’s health?
Labels:
awareness,
evaluation,
health communication,
public health
Wednesday, October 24, 2012
Rent The Runway Rocks Real Non-Airbrushed Models: Us!
 Like many of you, I have tried ordering clothes online. And it never goes well. They are always too tight or too long. They immediately make you feel bad about yourself. And of course- it is a huge pain to have to pack it up again and mail it back. And after all that- you still don't have anything to wear!! Weird, right? The clothes looked great in the pictures.
Like many of you, I have tried ordering clothes online. And it never goes well. They are always too tight or too long. They immediately make you feel bad about yourself. And of course- it is a huge pain to have to pack it up again and mail it back. And after all that- you still don't have anything to wear!! Weird, right? The clothes looked great in the pictures.The frustration of online shopping is a symptom of a larger problem. Many fashion lines are not made to fit the average woman. Rader Programs, a group of eating disorder treatment facilities, estimates that the average model weighs 117 pounds at 5'll and the average woman weighs 140 pounds at 5'4. No wonder my purchases are too tight and too long!
However, I'm feeling optimistic about change being possible in the fashion world. As of last week, Rent The Runway, an online service that lets users borrow current season high-fashion, has expanded their use of real women as models on their site. Users can upload pictures of themselves in the clothes, and include details about their height, weight, and chest size. The site will also have the capacity to allow users to search for women of similar body type, so that they can see how the clothes actually fit. I think this is fantastic. Not only will it hopefully cut down on the dreaded returns, but women will see models that look like them. It can reduce the shame and stigma that many women feel for lacking the 117 pounds at 5'll "ideal".
This initiative follows what I hope is a pattern of push back on pop culture for upholding women to unrealistic ideals that may lead to unhealthy body image. For example, we are seeing opposition to magazine airbrushing. Earlier this year, an ambitious eighth-grader put the pressure on Seventeen Magazine to review its policies on airbrushing and consider the impact it could have on young readers. Her online petition led the magazine to sign an eight-point "Body Peace Treaty", which outlined a commitment to never change models' body or face shapes.
We are seeing celebrities (especially recently!) disclosing their battles with eating disorders- often discussing the pressure they felt being in the entertainment industry. Over the past few months, we've heard from Katie Couric, Nicole Scherzinger, and Stacy London. Last year, Pop Health reviewed Portia De Rossi's book- Unbearable Lightness, which discussed her life-threatening eating disorder in much detail.
I hope that we are continuing to see a shift. I hope that there is less stigma in disclosing or discussing body image concerns and eating disorders. I also hope that the public continues to make their voices heard...whether they are fighting the magazine airbrush or the high fashion gown that will look terrible on anyone under 5'10.
What do you think: With the initiatives above and their predecessors (e.g., the Dove Campaign for Real Beauty)- do you see evidence of a shift in pop culture from "thin" to "real women"? What else needs to change to keep this initiative moving forward?
Labels:
celebrity,
eating disorders,
pop culture,
Rent The Runway,
stigma,
youth
Monday, October 1, 2012
The anatomy of a VAP test report
The vertical auto profile (VAP) test is an enhanced lipid profile test. It has been proposed, chiefly by the company Atherotech (), as a more complete test that relies on direct measurement of previously calculated lipid measures. The VAP test is particularly known for providing direct measurements of LDL cholesterol, instead of calculating them through equations ().
At the time of this writing, a typical VAP test report would provide direct measures of the cholesterol content of LDL, Lp(a), IDL, HDL, and VLDL particles. It would also provide additional measures referred to as secondary risk factors, notably particle density patterns and apolipoprotein concentrations. Finally, it would provide a customized risk summary and some basic recommendations for treatment. Below is the top part of a typical VAP test report (from Atherotech), showing measures of the cholesterol content of various particles. LDL cholesterol is combined for four particle subtypes, the small-dense subtypes 4 and 3, and the large-buoyant subtypes 2 and 1. A breakdown by LDL particle subtype is provided later in the VAP report.
In the table above, HDL cholesterol is categorized in two subtypes, the small-dense subtype 2, and the large-buoyant subtype 3. Interestingly, most of the HDL cholesterol in the table is supposedly of the least protective subtype, which seems to be a common finding in the general population. VLDL cholesterol is categorized in a similar way. IDL stands for intermediate-density lipoprotein; this is essentially a VLDL particle that has given off some of its content, particularly its triglyceride (or fat) cargo, but still remains in circulation.
Lp(a) is a special subtype of the LDL particle that is purported to be associated with markedly atherogenic factors. Mainstream medicine generally considers Lp(a) particles themselves to be atherogenic, which is highly debatable. Among other things, cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk and Lp(a) concentration follow a J-curve pattern, and Lp(a)’s range of variation in humans is very large. A blog post by Peter (Hyperlipid) has a figure right at the top that illustrates the former J-curve assertion (). The latter fact, related to range of variation, generally leads to a rather wide normal distribution of Lp(a) concentrations in most populations; meaning that a large number of individuals tend to fall outside Lp(a)’s optimal range and still have a low risk of developing CVD.
Below is the middle part of a typical VAP report, showing secondary risk factors, such as particle density patterns and apolipoprotein concentrations. LDL particle pattern A is considered to be the most protective, supposedly because large-buoyant LDL particles are less likely to penetrate the endothelial gaps, which are about 25 nm in diameter. Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind to fats for their transport in lipoproteins, to be used by various tissues for energy; free fatty acids also need to bind to proteins, notably albumin, to be transported to tissues for use as energy. Redundant particles and processes are everywhere in the human body!
Below is the bottom part of a typical VAP report, providing a risk summary and some basic recommendations. One of the recommendations is “to lower” the LDL target from 130mg/dL to 100mg/dL due to the presence of the checked emerging risk factors on the right, under “Considerations”. What that usually means in practice is a recommendation to take drugs, especially statins, to reduce LDL cholesterol levels. A recent post here and the discussion under it suggest that this would be a highly questionable recommendation in the vast majority of cases ().
What do I think about VAP tests? I think that they are useful in that they provide a lot more information about one’s lipids than standard lipid profiles, and more information is better than less. On the other hand, I think that people should be very careful about what they do with that information. There are even more direct tests that I would recommend before a decision to take drugs is made (, ), if that decision is ever made at all.
At the time of this writing, a typical VAP test report would provide direct measures of the cholesterol content of LDL, Lp(a), IDL, HDL, and VLDL particles. It would also provide additional measures referred to as secondary risk factors, notably particle density patterns and apolipoprotein concentrations. Finally, it would provide a customized risk summary and some basic recommendations for treatment. Below is the top part of a typical VAP test report (from Atherotech), showing measures of the cholesterol content of various particles. LDL cholesterol is combined for four particle subtypes, the small-dense subtypes 4 and 3, and the large-buoyant subtypes 2 and 1. A breakdown by LDL particle subtype is provided later in the VAP report.
In the table above, HDL cholesterol is categorized in two subtypes, the small-dense subtype 2, and the large-buoyant subtype 3. Interestingly, most of the HDL cholesterol in the table is supposedly of the least protective subtype, which seems to be a common finding in the general population. VLDL cholesterol is categorized in a similar way. IDL stands for intermediate-density lipoprotein; this is essentially a VLDL particle that has given off some of its content, particularly its triglyceride (or fat) cargo, but still remains in circulation.
Lp(a) is a special subtype of the LDL particle that is purported to be associated with markedly atherogenic factors. Mainstream medicine generally considers Lp(a) particles themselves to be atherogenic, which is highly debatable. Among other things, cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk and Lp(a) concentration follow a J-curve pattern, and Lp(a)’s range of variation in humans is very large. A blog post by Peter (Hyperlipid) has a figure right at the top that illustrates the former J-curve assertion (). The latter fact, related to range of variation, generally leads to a rather wide normal distribution of Lp(a) concentrations in most populations; meaning that a large number of individuals tend to fall outside Lp(a)’s optimal range and still have a low risk of developing CVD.
Below is the middle part of a typical VAP report, showing secondary risk factors, such as particle density patterns and apolipoprotein concentrations. LDL particle pattern A is considered to be the most protective, supposedly because large-buoyant LDL particles are less likely to penetrate the endothelial gaps, which are about 25 nm in diameter. Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind to fats for their transport in lipoproteins, to be used by various tissues for energy; free fatty acids also need to bind to proteins, notably albumin, to be transported to tissues for use as energy. Redundant particles and processes are everywhere in the human body!
Below is the bottom part of a typical VAP report, providing a risk summary and some basic recommendations. One of the recommendations is “to lower” the LDL target from 130mg/dL to 100mg/dL due to the presence of the checked emerging risk factors on the right, under “Considerations”. What that usually means in practice is a recommendation to take drugs, especially statins, to reduce LDL cholesterol levels. A recent post here and the discussion under it suggest that this would be a highly questionable recommendation in the vast majority of cases ().
What do I think about VAP tests? I think that they are useful in that they provide a lot more information about one’s lipids than standard lipid profiles, and more information is better than less. On the other hand, I think that people should be very careful about what they do with that information. There are even more direct tests that I would recommend before a decision to take drugs is made (, ), if that decision is ever made at all.
Monday, September 17, 2012
Familial hypercholesteromia: Why rely on cholesterol levels when more direct measures are available?
There are two forms of familial hypercholesteromia (FH), namely heterozygous and homozygous FH. In heterozygous FH only one copy of the gene that causes it is present, inherited either from the father or the mother. In homozygous FH, which is the most lethal form, two copies of the gene are present. FH is associated with early-onset cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Homozygous FH may happen if both the father and mother have heterozygous or homozygous FH. If both the father and mother have heterozygous FH, the likelihood that at least one in four children will have homozygous FH will be high. If both parents have homozygous FH the likelihood that all children will have homozygous FH will be high.
In fact, in the latter case, homozygous FH in the children is almost certain. One case in which it won’t occur is if the combining FH gene from the father or mother mutates into a non-FH gene before it is used in the assembly of the genome of the child. A gene mutation in a specific locus, only for the father or mother, is an unlikely event, and would lead to heterozygous FH. Two gene mutations at once in the same locus, for the father and mother, is a very unlikely event.
By the way, despite what many are led to believe based on fictional characters in movies and series like the X-Men and Hulk, mutations in functional genes usually lead to harmful traits. In our evolutionary past, those traits would have been largely removed from the gene pool by selection, making them rare or nonexistent in modern humans. Today we have modern medicine; a double-edged sword.
Mutations leading to super-human traits are very, very unlikely. The myostatin gene, for example, suppresses muscle growth. And yet the mutations that lead to little or no secretion of the related myostatin protein are very uncommon. Obviously they have not been favored by selection, even though their holders are very muscular – e.g., Germany’s “Incredible Hulky” ().
Okay, back to FH. Xanthelasmas are relatively common among those who suffer from FH (see photo below, from Globalskinatlas.com). They are skin deposits of cholesterol, have a genetic basis, and are NOT always associated with FH. This is important – several people have xanthelasmas but not FH.
FH is a fairly rare disease, even in its heterozygous form, with an overall incidence of approximately 0.2 percent. That is, about 1 in 500 people in the general population will have it. Genetically related groups will see a much higher or lower rate of incidence, as the disease is strongly influenced by a genetic mutation. This genetic mutation is apparently in the LDL receptor gene, located on the short arm of chromosome 19.
The table below, from a study by Miltiadous and colleagues (), paints a broad picture of the differences one would typically see between heterozygous FH sufferers and non-FH controls.
The main difference is in total cholesterol and in the relatively large contribution of LDL to total cholesterol. A large difference is also seen in Apolipoprotein B (indicated as "Apo B"), which acts as a LDL transporter (not to be confused with a LDL receptor). The LDL cholesterol shown on the table is calculated through the Friedewald equation, which is notoriously imprecise at low triglyceride levels ().
Looking at the total cholesterol row on the table, and assuming that the numbers after the plus/minus signs are standard deviations, we can conclude that: (a) a little more than two-thirds of the heterozygous FH sufferers had total cholesterol levels falling in between 280 and 446; and (b) a little more than two-thirds of the non-FH controls had total cholesterol levels falling in between 135 and 225.
Keep in mind that about 13.5 percent {calculated as: (95-68)/2} of the non-FH controls had total cholesterol levels between 225 and 270. This is a nontrivial percentage; i.e., these may be a minority but are not rare individuals. Heterozygous FH sufferers are rare, at 0.2 percent of the general population. Moreover, about 2 percent of the non-FH controls had non-pathological total cholesterol levels between 270 and 315. That is not so rare either, amounting to an “incidence” 10 times higher than heterozygous FH.
What would happen if people with heterozygous FH were to replace refined carbohydrates and sugars with saturated fat and cholesterol in their diets? Very likely their already high total cholesterol would go up higher, in part because their HDL cholesterol would go up (). Still, how could they be sure that CVD progression would accelerate if they did that?
According to some studies, the higher HDL cholesterol would either be generally protective or associated with protective factors, even among those with FH (). One of those protective factors may be a more nutrient-dense diet, as many foods rich in cholesterol are very nutrient-dense – e.g., eggs, organ meats, and seafood.
This brings me to my main point in this post. It is mainstream practice to diagnose people with FH based on total and/or LDL cholesterol levels. But the main problem with FH is that it leads to early onset of CVD, which can be measured more directly through simple tests, such as intima-media thickness and related ultrasound plaque tests (). These are noninvasive tests, done in 5 minutes or so, and often covered by insurance.
Even if simple direct tests are not perfect, it seems utterly nonsensical to rely on cholesterol measures to diagnose and treat FH, given the possible overlap between pathological and non-pathological high total cholesterol levels.
Homozygous FH may happen if both the father and mother have heterozygous or homozygous FH. If both the father and mother have heterozygous FH, the likelihood that at least one in four children will have homozygous FH will be high. If both parents have homozygous FH the likelihood that all children will have homozygous FH will be high.
In fact, in the latter case, homozygous FH in the children is almost certain. One case in which it won’t occur is if the combining FH gene from the father or mother mutates into a non-FH gene before it is used in the assembly of the genome of the child. A gene mutation in a specific locus, only for the father or mother, is an unlikely event, and would lead to heterozygous FH. Two gene mutations at once in the same locus, for the father and mother, is a very unlikely event.
By the way, despite what many are led to believe based on fictional characters in movies and series like the X-Men and Hulk, mutations in functional genes usually lead to harmful traits. In our evolutionary past, those traits would have been largely removed from the gene pool by selection, making them rare or nonexistent in modern humans. Today we have modern medicine; a double-edged sword.
Mutations leading to super-human traits are very, very unlikely. The myostatin gene, for example, suppresses muscle growth. And yet the mutations that lead to little or no secretion of the related myostatin protein are very uncommon. Obviously they have not been favored by selection, even though their holders are very muscular – e.g., Germany’s “Incredible Hulky” ().
Okay, back to FH. Xanthelasmas are relatively common among those who suffer from FH (see photo below, from Globalskinatlas.com). They are skin deposits of cholesterol, have a genetic basis, and are NOT always associated with FH. This is important – several people have xanthelasmas but not FH.
FH is a fairly rare disease, even in its heterozygous form, with an overall incidence of approximately 0.2 percent. That is, about 1 in 500 people in the general population will have it. Genetically related groups will see a much higher or lower rate of incidence, as the disease is strongly influenced by a genetic mutation. This genetic mutation is apparently in the LDL receptor gene, located on the short arm of chromosome 19.
The table below, from a study by Miltiadous and colleagues (), paints a broad picture of the differences one would typically see between heterozygous FH sufferers and non-FH controls.
The main difference is in total cholesterol and in the relatively large contribution of LDL to total cholesterol. A large difference is also seen in Apolipoprotein B (indicated as "Apo B"), which acts as a LDL transporter (not to be confused with a LDL receptor). The LDL cholesterol shown on the table is calculated through the Friedewald equation, which is notoriously imprecise at low triglyceride levels ().
Looking at the total cholesterol row on the table, and assuming that the numbers after the plus/minus signs are standard deviations, we can conclude that: (a) a little more than two-thirds of the heterozygous FH sufferers had total cholesterol levels falling in between 280 and 446; and (b) a little more than two-thirds of the non-FH controls had total cholesterol levels falling in between 135 and 225.
Keep in mind that about 13.5 percent {calculated as: (95-68)/2} of the non-FH controls had total cholesterol levels between 225 and 270. This is a nontrivial percentage; i.e., these may be a minority but are not rare individuals. Heterozygous FH sufferers are rare, at 0.2 percent of the general population. Moreover, about 2 percent of the non-FH controls had non-pathological total cholesterol levels between 270 and 315. That is not so rare either, amounting to an “incidence” 10 times higher than heterozygous FH.
What would happen if people with heterozygous FH were to replace refined carbohydrates and sugars with saturated fat and cholesterol in their diets? Very likely their already high total cholesterol would go up higher, in part because their HDL cholesterol would go up (). Still, how could they be sure that CVD progression would accelerate if they did that?
According to some studies, the higher HDL cholesterol would either be generally protective or associated with protective factors, even among those with FH (). One of those protective factors may be a more nutrient-dense diet, as many foods rich in cholesterol are very nutrient-dense – e.g., eggs, organ meats, and seafood.
This brings me to my main point in this post. It is mainstream practice to diagnose people with FH based on total and/or LDL cholesterol levels. But the main problem with FH is that it leads to early onset of CVD, which can be measured more directly through simple tests, such as intima-media thickness and related ultrasound plaque tests (). These are noninvasive tests, done in 5 minutes or so, and often covered by insurance.
Even if simple direct tests are not perfect, it seems utterly nonsensical to rely on cholesterol measures to diagnose and treat FH, given the possible overlap between pathological and non-pathological high total cholesterol levels.
Monday, September 3, 2012
Daniel Suelo, the man who quit money, seems remarkably healthy
Daniel James Shellabarger (better known as Daniel Suelo) is portrayed in the bestselling 2012 nonfiction book by Mark Sundeen titled “The Man Who Quit Money” ().
Apparently Suelo stopped using money in 2000, and lives in a cave near the city of Moab in Utah. His diet comprises primarily wild vegetables and fruits, insects, and road kill; as well as discarded or donated food he gets from others when he visits the city. The photo below is from a recent BBC documentary. An interesting 2006 YouTube clip on Suelo is titled “Moneyless in Moab” ().
Suelo is listed as having been born in 1961 (), and the photo above appears to have been taken in 2012. If these dates are correct, he is 51 in the photo above. I cannot help but think that he looks remarkably healthy. The 40-50 age period is one that often sets the stage for many diseases of civilization in urban societies.
Suelo’s decision seems like a radical one, at least to me. There are always complex motivations behind radical decisions. In the case of Suelo, some of these motivations are captured in the comment below, which is part of a review of the book “The Man Who Quit Money” posted on Amazon.com by a reader.
Many people have been inspired by Suelo’s story, to some extent because they see that adopting a radical form of “simple living” () may not only be possible but also liberating. Obviously Suelo’s lifestyle, as it is now, would not be possible without the help of others who adopt a more “traditional” lifestyle. Below is a critical review by a reader of the book, posted on Amazon.com, which harshly reflects this perspective.
Still, Suelo’s story is interesting, including from a human health perspective. An article on Details.com by Christopher Ketcham provides a glimpse at what a day in Suelo’s life looks like (). It seems that on most days he has one main meal per day.
It is hard to get a sense of the nutrient composition of his diet. It looks like his diet is limited in but not devoid of industrial foods, and one in which food consumption is sporadic, opportunistic, and driven primarily by hunger and availability – not by stress or set meal times, for example.
He probably walks a lot; his cave is one hour away from Moab by foot, and it looks like he goes to Moab often. Apparently he almost never gets sick.
Suelo also writes a blog (), which has many followers, and also maintains other websites, from the Public Library in Moab. His first blog post has over 1,000 comments under it ().
Apparently Suelo stopped using money in 2000, and lives in a cave near the city of Moab in Utah. His diet comprises primarily wild vegetables and fruits, insects, and road kill; as well as discarded or donated food he gets from others when he visits the city. The photo below is from a recent BBC documentary. An interesting 2006 YouTube clip on Suelo is titled “Moneyless in Moab” ().
Suelo is listed as having been born in 1961 (), and the photo above appears to have been taken in 2012. If these dates are correct, he is 51 in the photo above. I cannot help but think that he looks remarkably healthy. The 40-50 age period is one that often sets the stage for many diseases of civilization in urban societies.
Suelo’s decision seems like a radical one, at least to me. There are always complex motivations behind radical decisions. In the case of Suelo, some of these motivations are captured in the comment below, which is part of a review of the book “The Man Who Quit Money” posted on Amazon.com by a reader.
[…] a picture of Suelo not as an untarnished hero, but a man who has wrestled with heartbreak, depression, disillusionment with his family's faith, and his repugnance to working for the pure sake of making money and buying things. Whether or not you are inspired to follow Suelo's example, this book will make you think.
Many people have been inspired by Suelo’s story, to some extent because they see that adopting a radical form of “simple living” () may not only be possible but also liberating. Obviously Suelo’s lifestyle, as it is now, would not be possible without the help of others who adopt a more “traditional” lifestyle. Below is a critical review by a reader of the book, posted on Amazon.com, which harshly reflects this perspective.
Any infantile mentality charmed by this inane story should simply generalize the message - visualize a world in which all of us live like the parasitic protagonist. How fortunate for Suelo that there are still people who engage in productive work and indirectly and unknowingly keep the human sponge alive […] Suelo never quit money he simply quit contributing anything and continues to survive simply as a parasite.
Still, Suelo’s story is interesting, including from a human health perspective. An article on Details.com by Christopher Ketcham provides a glimpse at what a day in Suelo’s life looks like (). It seems that on most days he has one main meal per day.
It is hard to get a sense of the nutrient composition of his diet. It looks like his diet is limited in but not devoid of industrial foods, and one in which food consumption is sporadic, opportunistic, and driven primarily by hunger and availability – not by stress or set meal times, for example.
He probably walks a lot; his cave is one hour away from Moab by foot, and it looks like he goes to Moab often. Apparently he almost never gets sick.
Suelo also writes a blog (), which has many followers, and also maintains other websites, from the Public Library in Moab. His first blog post has over 1,000 comments under it ().
Labels:
comfortable furniture,
Daniel Suelo,
depression,
fasting,
interesting people,
intermittent fasting,
simple living
Monday, August 27, 2012
Madonna's "MDNA Show Manifesto" Defends Using Guns on Tour: Do You Agree?
As we speak, Madonna is en route to my city- Philadelphia, to launch the North American leg of her "MDNA World Tour". In advance of her arrival, she has released a statement to the local Metro defending one of the most controversial parts of her tour...the use of fake firearms in concert. Here is a portion of that statement:
"It's true there is a lot of violence in the beginning of the show and sometimes the use of fake guns - but they are used as metaphors. I do not condone violence or the use of guns. Rather they are symbols of wanting to appear strong and wanting to find a way to stop feelings that I find hurtful or damaging. In my case its wanting to stop the lies and hypocrisy of the church, the intolerance of many narrow minded cultures and societies I have experienced throughout my life and in some cases the pain I have felt from having my heart broken".
Gun violence is (unfortunately) not a new problem. However, the topic is quite timely due to increased U.S. media coverage following several mass shootings in the past few weeks- Aurora, CO, Oak Creek, WI, and New York, NY. The issue of gun violence has reached crisis levels in Philadelphia where Madonna will be performing. A new open source journalism project called http://guncrisis.org/ "contends that there is an epidemic of homicide by gunfire in Philadelphia and similar cities". They are seeking solutions.
The solutions being sought by GunCrisis: Philadelphia and others involve taking a public health approach to gun violence. The recent high profile shootings have produced several well-written pieces about gun violence and what we need to do next:
Do you believe that the gun "saturation" goes beyond those in our homes to include those used for entertainment? E.g., Guns in movies or video games; Madonna's concert props
Is Madonna successful? Does using guns as a metaphorical image help her reach her goals and battle against hypocrisy and intolerance?
In addition to those listed above, what other strategies should we incorporate into a public health approach against gun violence?
"It's true there is a lot of violence in the beginning of the show and sometimes the use of fake guns - but they are used as metaphors. I do not condone violence or the use of guns. Rather they are symbols of wanting to appear strong and wanting to find a way to stop feelings that I find hurtful or damaging. In my case its wanting to stop the lies and hypocrisy of the church, the intolerance of many narrow minded cultures and societies I have experienced throughout my life and in some cases the pain I have felt from having my heart broken".
Gun violence is (unfortunately) not a new problem. However, the topic is quite timely due to increased U.S. media coverage following several mass shootings in the past few weeks- Aurora, CO, Oak Creek, WI, and New York, NY. The issue of gun violence has reached crisis levels in Philadelphia where Madonna will be performing. A new open source journalism project called http://guncrisis.org/ "contends that there is an epidemic of homicide by gunfire in Philadelphia and similar cities". They are seeking solutions.
The solutions being sought by GunCrisis: Philadelphia and others involve taking a public health approach to gun violence. The recent high profile shootings have produced several well-written pieces about gun violence and what we need to do next:
- Prompt policy discussions about easy access to ammunition, high-capacity magazines, and assault weapons.
- Use our public health skills to conduct further research into the causes of firearm injuries.
- Examine gun violence as a social disease- one that stems from a society "saturated with guns".
Do you believe that the gun "saturation" goes beyond those in our homes to include those used for entertainment? E.g., Guns in movies or video games; Madonna's concert props
Is Madonna successful? Does using guns as a metaphorical image help her reach her goals and battle against hypocrisy and intolerance?
In addition to those listed above, what other strategies should we incorporate into a public health approach against gun violence?
Labels:
guns,
injuries,
Madonna,
Philadelphia,
pop culture,
public health
Monday, August 20, 2012
The 2012 Atherosclerosis egg study: Plaque decreased as LDL increased with consumption of 2.3 eggs per week or more
A new study by David Spence and colleagues, published online in July 2012 in the journal Atherosclerosis (), has been gaining increasing media attention (e.g., ). The article is titled: “Egg yolk consumption and carotid plaque”. As the title implies, the study focuses on egg yolk consumption and its association with carotid artery plaque buildup.
The study argues that “regular consumption of egg yolk should be avoided by persons at risk of cardiovascular disease”. It hints at egg yolks being unhealthy in general, possibly even more so than cigarettes. Solid critiques have already been posted on blogs by Mark Sisson, Chris Masterjohn, and Zoe Harcombe (, , ), among others.
These critiques present valid arguments for why the key findings of the study cannot be accepted, especially the finding that eggs are more dangerous to one’s health than cigarettes. This post is a bit different. It uses the data reported in the study to show that it (the data) suggests that egg consumption is actually health-promoting.
I used the numbers in Table 2 of the article to conduct a test that is rarely if ever conducted in health studies – a moderating effect test. I left out the “egg-yolk years” variable used by the authors, and focused on weekly egg consumption (see Chris’s critique). My analysis, using WarpPLS (), had to be done only visually, because using values from Table 2 meant that I had access only to data on a few variables organized in quintiles. That is, my analysis here using aggregate data is an N=5 analysis; a small sample indeed. The full-text article is not available publicly; Zoe was kind enough to include the data from Table 2 in her critique post.
Below is the model that I used for the moderating effect test. It allowed me to look into the effect that the variable EggsWk (number of eggs consumed per week) had on the association between LDL (LDL cholesterol) and Plaque (carotid plaque). This type of effect, namely a moderating effect, is confusing to many people, because it is essentially the effect that a variable has on the effect of another variable on a third. Still, being confusing does not mean being less important. I should note that this type of effect is similar to a type of conditional association tested via Bayesian statistics – if one eats more eggs, what is the association between having a high LDL cholesterol and plaque buildup?
You can see what is happening visually on the graph below. The plot on the left side is for low weekly egg consumption. In it, the association between LDL cholesterol and plaque is positive – eating fewer eggs, plaque and LDL increase together. The plot on the right side is for high weekly egg consumption. In this second plot, the association between LDL cholesterol and plaque is negative – eating more eggs, plaque decreases as LDL increases. And what is the turning point? It is about 2.3 eggs per week.
So the “evil” particle, the LDL, is playing tricks with us; but thankfully the wonderful eggs come to the rescue, right? Well, it looks a bit like it, but maybe other foods would have a similar effect. In part because of the moderating effect discussed above, the multivariate association between LDL cholesterol and plaque was overall negative. This multivariate association was estimated controlling for the moderating effect of weekly egg consumption. You can see this on the plot below.
The highest amount of plaque is at the far left of the plot. It is associated with the lowest LDL cholesterol quintile. (So much for eggs causing plaque via LDL cholesterol eh!?) What is happening here? Maybe egg consumption above a certain level shifts the size of the LDL particles from small to large, making the potentially atherogenic ones harmless. (Saturated fat consumption, in the context of a nutritious diet in lean individuals, seems to have a similar effect.) Maybe eggs contain nutrients that promote overall health, leading LDL particles to "behave" and do what they are supposed to do. Maybe it is a combination of these and other effects.
The study argues that “regular consumption of egg yolk should be avoided by persons at risk of cardiovascular disease”. It hints at egg yolks being unhealthy in general, possibly even more so than cigarettes. Solid critiques have already been posted on blogs by Mark Sisson, Chris Masterjohn, and Zoe Harcombe (, , ), among others.
These critiques present valid arguments for why the key findings of the study cannot be accepted, especially the finding that eggs are more dangerous to one’s health than cigarettes. This post is a bit different. It uses the data reported in the study to show that it (the data) suggests that egg consumption is actually health-promoting.
I used the numbers in Table 2 of the article to conduct a test that is rarely if ever conducted in health studies – a moderating effect test. I left out the “egg-yolk years” variable used by the authors, and focused on weekly egg consumption (see Chris’s critique). My analysis, using WarpPLS (), had to be done only visually, because using values from Table 2 meant that I had access only to data on a few variables organized in quintiles. That is, my analysis here using aggregate data is an N=5 analysis; a small sample indeed. The full-text article is not available publicly; Zoe was kind enough to include the data from Table 2 in her critique post.
Below is the model that I used for the moderating effect test. It allowed me to look into the effect that the variable EggsWk (number of eggs consumed per week) had on the association between LDL (LDL cholesterol) and Plaque (carotid plaque). This type of effect, namely a moderating effect, is confusing to many people, because it is essentially the effect that a variable has on the effect of another variable on a third. Still, being confusing does not mean being less important. I should note that this type of effect is similar to a type of conditional association tested via Bayesian statistics – if one eats more eggs, what is the association between having a high LDL cholesterol and plaque buildup?
You can see what is happening visually on the graph below. The plot on the left side is for low weekly egg consumption. In it, the association between LDL cholesterol and plaque is positive – eating fewer eggs, plaque and LDL increase together. The plot on the right side is for high weekly egg consumption. In this second plot, the association between LDL cholesterol and plaque is negative – eating more eggs, plaque decreases as LDL increases. And what is the turning point? It is about 2.3 eggs per week.
So the “evil” particle, the LDL, is playing tricks with us; but thankfully the wonderful eggs come to the rescue, right? Well, it looks a bit like it, but maybe other foods would have a similar effect. In part because of the moderating effect discussed above, the multivariate association between LDL cholesterol and plaque was overall negative. This multivariate association was estimated controlling for the moderating effect of weekly egg consumption. You can see this on the plot below.
The highest amount of plaque is at the far left of the plot. It is associated with the lowest LDL cholesterol quintile. (So much for eggs causing plaque via LDL cholesterol eh!?) What is happening here? Maybe egg consumption above a certain level shifts the size of the LDL particles from small to large, making the potentially atherogenic ones harmless. (Saturated fat consumption, in the context of a nutritious diet in lean individuals, seems to have a similar effect.) Maybe eggs contain nutrients that promote overall health, leading LDL particles to "behave" and do what they are supposed to do. Maybe it is a combination of these and other effects.
Labels:
atherosclerosis,
cholesterol,
egg,
LDL,
plaque,
saturated fat
Wednesday, August 15, 2012
Usage Of Henna On Your Hair...
* If you use henna regularly, you will find that the graying of hair will also
get reduced.
* Take a plastic bowl and take henna in sufficient quantity. Add slightly
get reduced.
* Take a plastic bowl and take henna in sufficient quantity. Add slightly
warm water and some lemon juice to it and mix thoroughly so that it
mixes consistently and becomes a paste. Leave the mixture overnight
so that the dye works well on hair.
* Add the ingredients properly and if you have dry hair you can add few
drops of mustard oil to it. For oily hair only lemon juice is sufficient.
You can add 2 teaspoons of yogurt if you have dandruff in your hair.
* Wash your hair before applying the henna paste. Make sure you wear
old clothes before applying henna on your hair because it leaves
* Add the ingredients properly and if you have dry hair you can add few
drops of mustard oil to it. For oily hair only lemon juice is sufficient.
You can add 2 teaspoons of yogurt if you have dandruff in your hair.
* Wash your hair before applying the henna paste. Make sure you wear
old clothes before applying henna on your hair because it leaves
black stains.
* You can wear hand gloves so that you can prevent your hands from
getting stained.
* If you have long hair, you can part your hair from middle and start
applying the henna paste. Cover all the parts and apply to the full
length of your hair.
* Leave the henna applied hair for one or two hours as you need the
colour to come out and then wash it with running water. Once the paste
is removed, you can apply a mild shampoo and let the hair dry naturally.
* You can wear hand gloves so that you can prevent your hands from
getting stained.
* If you have long hair, you can part your hair from middle and start
applying the henna paste. Cover all the parts and apply to the full
length of your hair.
* Leave the henna applied hair for one or two hours as you need the
colour to come out and then wash it with running water. Once the paste
is removed, you can apply a mild shampoo and let the hair dry naturally.
Tuesday, August 14, 2012
Ancestral Health Symposium 2012: Evolutionarily sound diets and lifestyles may revolutionize health care
The Ancestral Health Symposium 2012 was very interesting on many levels. Aaron Blaisdell and the team of volunteers really did a superb job at organizing the Symposium. Boston is a great city with an excellent public transportation system, something that is always great for meetings, and a great choice for the Symposium. Needless to say, so was Harvard. Even though the program was packed there were plenty of opportunities to meet and talk with several people during the breaks.
We had our panel “New Technologies and New Opportunities”, which Paul Jaminet moderated. The panelists were Chris Keller, Chris Kresser, Dan Pardi, and myself. The first photo below, by Bobby Gill, shows Chris Keller speaking; I am on the far left looking at the screen. The second photo, by Beth Mazur, shows all the panelists. The third photo, also by Bobby Gill, shows a group of us talking to Stephan Guyenet after his presentation.
I talked a bit toward the end of the panel about the importance of taking nonlinearity into consideration in analyses of health data, but ended up being remembered later for saying that “men are women with a few design flaws”. I said that to highlight the strong protective effect of being female in terms of health, which was clear from the model I was discussing.
There is a good evolutionary reason for the protective effect of being female. Evolution is a population phenomenon. Genes do not evolve; neither do individuals. Populations evolve through the spread or disappearance of genotypes. A healthy population with 99 men and 1 woman will probably disappear quickly, and so will its gene pool. A healthy population with 99 women and 1 man will probably thrive, even with the drag of inbreeding depression. Under harsh environmental conditions, the rate of female-to-male births goes up, in some cases quite a lot.
I was able to talk to, or at least meet briefly face-to-face with, many of the people that I have interacted with online on this blog and other blogs. Just to name a few: Miki Ben-Dor, Aaron Blaisdell, Emily Deans, Andreas Eenfeldt, Glenn Ellmers, Benjamin Gebhard, Stephan Guyenet, Dallas Hartwig, Melissa Hartwig, Paul Jaminet, Chris Keller, Chris Kresser, Mathieu Lalonde, Robert Lustig, Chris Masterjohn, Beth Mazur, Denise Minger, Jimmy Moore, Katherine Morrison, Richard Nikoley, Dan Pardi, Kamal Patel, David Pendergrass, Mark Sisson, Mary Beth Smrtic, J. Stanton, Carlos Andres Toro, and Grayson Wheatley.
It would have been nice to have Peter (from Hyperlipid) there, as I think a lot of the attendants are fans. I attended Jamie Scott’s very interesting talk, but ended up not being able to chat with him. This is a pity because we share some common experiences – e.g., I lived in New Zealand for a few years. I did have the opportunity to talk at some length with J. Stanton, who is an inspiration. It was also great to exchange some ideas with my panelists, Miki Ben-Dor, Emily Deans, Stephan Guyenet, Chris Masterjohn, Kamal Patel, and David Pendergrass. I wish I had more time to talk with Denise Minger, who is clearly a very nice person in addition to being very smart. Talking about a smart person, it was also nice chatting a bit with Richard Nikoley; a successful entrepreneur who is in the enviable position of doing what he feels like doing.
I could not help but notice a tendency among some participants (perhaps many, judging from online threads) to pay a lot of attention to how other people looked in a very judgmental way. That person is too fat, his/her face is too red, she/he looks too old etc. So was this supposed to be the Ancestral Health Pageant 2012? There is nothing wrong with looking good. But many people adopt an evolution-inspired lifestyle because they are quite unhealthy to start with. And this includes some of the presenters. It takes time to change one’s health, relapses occur, and no one is getting younger. Moreover, some of the presenters’ ideas and advice may have much more dramatic positive effects on people other than themselves, because of their own pre-existing conditions. The ideas and advice are still solid.
A message that I think this Symposium conveyed particularly well was that an evolutionarily sound diet and lifestyle can truly revolutionize our health care system. Robb Wolf’s talk in particular, based on his recent experience in Nevada with law enforcement officers, made this point very effectively. The title of the talk is “How Markets and Evolution Can Revolutionize Medicine”. One very interesting idea he put forth was that establishments like gyms could expand the range of support activities they offer their customers, officially becoming the beginning of the health care chain. There are already health insurance plans that offer premium reductions for those who go to gyms. Being part of the health care chain would be different and a significant step forward - diet and exercise are powerful "drugs".
One thing that caught me a bit off-guard was Robb’s strong advocacy of the use of a drug, namely metformin (a.k.a. glucophage); even preventively in some special cases, such as with sleep-deprived law enforcement officers. I have to listen to that talk again when it is up online, to make sure that I understood it correctly. It seems to me that changing the nature of shift work among law enforcement officers, at least partially, may be a better target; current practices appear not only to impair the officers’ health but also their effectiveness in law enforcement activities. Besides, I think we need to better understand the nature and functions of cortisol, which is viewed by many as a hormone that exists only to do us harm.
Sleep deprivation is associated with an elevation in cortisol production. Elevated cortisol levels lead over time to visceral fat accumulation, which promotes systemic inflammation. Systemic inflammation is possibly the root cause of most diseases of civilization. But cortisol itself has powerful anti-inflammatory properties, and visceral fat is generally easy to mobilize through intense exercise – probably one of the key reasons why we have visceral fat. I think we need to understand this situation a bit better before thinking about preventive uses of metformin, which nevertheless is a drug that seems to do wonders in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Beth Mazur was kind enough to put up a post with links to various Ancestral Health Symposium 2012 summary posts, as well as pictures. Paul Jaminet has a post with an insightful discussion of our panel at the Symposium.
We had our panel “New Technologies and New Opportunities”, which Paul Jaminet moderated. The panelists were Chris Keller, Chris Kresser, Dan Pardi, and myself. The first photo below, by Bobby Gill, shows Chris Keller speaking; I am on the far left looking at the screen. The second photo, by Beth Mazur, shows all the panelists. The third photo, also by Bobby Gill, shows a group of us talking to Stephan Guyenet after his presentation.
I talked a bit toward the end of the panel about the importance of taking nonlinearity into consideration in analyses of health data, but ended up being remembered later for saying that “men are women with a few design flaws”. I said that to highlight the strong protective effect of being female in terms of health, which was clear from the model I was discussing.
There is a good evolutionary reason for the protective effect of being female. Evolution is a population phenomenon. Genes do not evolve; neither do individuals. Populations evolve through the spread or disappearance of genotypes. A healthy population with 99 men and 1 woman will probably disappear quickly, and so will its gene pool. A healthy population with 99 women and 1 man will probably thrive, even with the drag of inbreeding depression. Under harsh environmental conditions, the rate of female-to-male births goes up, in some cases quite a lot.
I was able to talk to, or at least meet briefly face-to-face with, many of the people that I have interacted with online on this blog and other blogs. Just to name a few: Miki Ben-Dor, Aaron Blaisdell, Emily Deans, Andreas Eenfeldt, Glenn Ellmers, Benjamin Gebhard, Stephan Guyenet, Dallas Hartwig, Melissa Hartwig, Paul Jaminet, Chris Keller, Chris Kresser, Mathieu Lalonde, Robert Lustig, Chris Masterjohn, Beth Mazur, Denise Minger, Jimmy Moore, Katherine Morrison, Richard Nikoley, Dan Pardi, Kamal Patel, David Pendergrass, Mark Sisson, Mary Beth Smrtic, J. Stanton, Carlos Andres Toro, and Grayson Wheatley.
It would have been nice to have Peter (from Hyperlipid) there, as I think a lot of the attendants are fans. I attended Jamie Scott’s very interesting talk, but ended up not being able to chat with him. This is a pity because we share some common experiences – e.g., I lived in New Zealand for a few years. I did have the opportunity to talk at some length with J. Stanton, who is an inspiration. It was also great to exchange some ideas with my panelists, Miki Ben-Dor, Emily Deans, Stephan Guyenet, Chris Masterjohn, Kamal Patel, and David Pendergrass. I wish I had more time to talk with Denise Minger, who is clearly a very nice person in addition to being very smart. Talking about a smart person, it was also nice chatting a bit with Richard Nikoley; a successful entrepreneur who is in the enviable position of doing what he feels like doing.
I could not help but notice a tendency among some participants (perhaps many, judging from online threads) to pay a lot of attention to how other people looked in a very judgmental way. That person is too fat, his/her face is too red, she/he looks too old etc. So was this supposed to be the Ancestral Health Pageant 2012? There is nothing wrong with looking good. But many people adopt an evolution-inspired lifestyle because they are quite unhealthy to start with. And this includes some of the presenters. It takes time to change one’s health, relapses occur, and no one is getting younger. Moreover, some of the presenters’ ideas and advice may have much more dramatic positive effects on people other than themselves, because of their own pre-existing conditions. The ideas and advice are still solid.
A message that I think this Symposium conveyed particularly well was that an evolutionarily sound diet and lifestyle can truly revolutionize our health care system. Robb Wolf’s talk in particular, based on his recent experience in Nevada with law enforcement officers, made this point very effectively. The title of the talk is “How Markets and Evolution Can Revolutionize Medicine”. One very interesting idea he put forth was that establishments like gyms could expand the range of support activities they offer their customers, officially becoming the beginning of the health care chain. There are already health insurance plans that offer premium reductions for those who go to gyms. Being part of the health care chain would be different and a significant step forward - diet and exercise are powerful "drugs".
One thing that caught me a bit off-guard was Robb’s strong advocacy of the use of a drug, namely metformin (a.k.a. glucophage); even preventively in some special cases, such as with sleep-deprived law enforcement officers. I have to listen to that talk again when it is up online, to make sure that I understood it correctly. It seems to me that changing the nature of shift work among law enforcement officers, at least partially, may be a better target; current practices appear not only to impair the officers’ health but also their effectiveness in law enforcement activities. Besides, I think we need to better understand the nature and functions of cortisol, which is viewed by many as a hormone that exists only to do us harm.
Sleep deprivation is associated with an elevation in cortisol production. Elevated cortisol levels lead over time to visceral fat accumulation, which promotes systemic inflammation. Systemic inflammation is possibly the root cause of most diseases of civilization. But cortisol itself has powerful anti-inflammatory properties, and visceral fat is generally easy to mobilize through intense exercise – probably one of the key reasons why we have visceral fat. I think we need to understand this situation a bit better before thinking about preventive uses of metformin, which nevertheless is a drug that seems to do wonders in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Beth Mazur was kind enough to put up a post with links to various Ancestral Health Symposium 2012 summary posts, as well as pictures. Paul Jaminet has a post with an insightful discussion of our panel at the Symposium.
Labels:
Ancestral Health Symposium,
cortisol,
metformin,
sleep
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)